There are many people around us of different age groups that are either diagnosed or have underlying symptoms of autism. Autism is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by challenges with social communication, and by restricted and repetitive behaviours. is now considered part of the wider autism spectrum. People with autism have trouble with communication. They have trouble understanding what other people think and feel. This makes it hard for them to express themselves, either with words or through gestures, facial expressions, and touch. People with autism might have problems with learning. Their skills might develop unevenly. For example, they could have trouble communicating but be unusually good at art, music, math, or memory. Because of this, they might do especially well on tests of analysis or problem-solving. More children are diagnosed with autism now than ever before. But the latest numbers could be higher because of changes in how it’s diagnosed, not because more children have a disorder.
Autism is known to affect every one in every 60 individuals and boys are said to have more risk of developing it than girls. It can be hard to get a definite diagnosis of autism. Your doctor will focus on behaviour and development.
A developmental screening will tell the doctor whether a child is on track with basic skills like learning, speaking, behavior, and moving. If a child shows signs of a problem on these screenings, they’ll need a more complete evaluation. This might include hearing and vision tests or genetic tests. Your doctor might want to bring in someone who specializes in autism disorders, like a developmental paediatrician or a child psychologist. Some psychologists can also give a test called the Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule (ADOS).parents can also find some symptoms and unusual behaviour


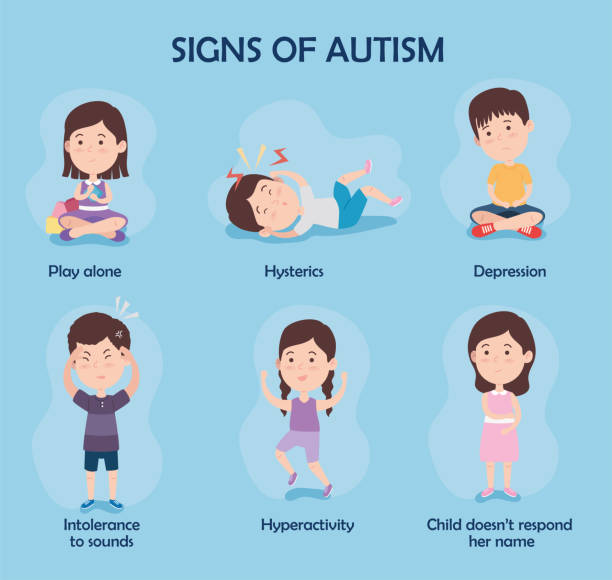
Common symptoms of autism include:
- A lack of eye contact
- A narrow range of interests or intense interest in certain topics
- Doing something over and over, like repeating words or phrases, rocking back and forth, or flipping a lever
- High sensitivity to sounds, touches, smells, or sights that seem ordinary to other people
- Not looking at or listening to other people
- Not looking at things when another person points at them
- Not wanting to be held or cuddled
- Problems understanding or using speech, gestures, facial expressions, or tone of voice
- Talking in a sing-song, flat, or robotic voice
- Trouble adapting to changes in routine
What Are the Types of Autism Spectrum Disorders?
These types were once thought to be separate conditions. Now, they fall under the range of autism spectrum disorders including:
Asperger’s syndrome. These children don’t have a problem with language; in fact, they tend to score in the average or above-average range on intelligence tests. But they have social problems and a narrow scope of interests.
Autistic disorder. This is what most people think of when they hear the word “autism.” It refers to problems with social interactions, communication, and play in children younger than 3 years.
Childhood disintegrative disorder. These children have typical development for at least 2 years and then lose some or most of their communication and social skills.
Pervasive developmental disorder (PDD or atypical autism). Your doctor might use this term if your child has some autistic behavior, like delays in social and communications skills, but doesn’t fit into another category.

What Causes Autism?
Exactly why autism happens isn’t clear. It could stem from problems in parts of your brain that interpret sensory input and process language.. It can happen in people of any race, ethnicity, or social background. Family income, lifestyle, or educational level doesn’t affect a child’s risk of autism. Autism runs in families, so certain combinations of genes may increase a child’s risk. A child with an older parent has a higher risk of autism. Pregnant women who are exposed to certain drugs or chemicals, like alcohol or anti-seizure medications, are more likely to have autistic children. Other risk factors include maternal metabolic conditions such as diabetes and obesity. Research has also linked autism to untreated phenylketonuria (also called PKU, a metabolic disorder caused by the absence of an enzyme) and rubella (German measles).There is no evidence that vaccinations cause autism.
How Is Autism Treated?
There’s no cure for autism. But early treatment can make a big difference in development for a child with autism. If you think your child shows symptoms of ASD, tell your doctor as soon as possible.What works for one person might not work for another. Your doctor should tailor treatment for you or your child. The two main types of treatments are:
Behavioral and communication therapy to help with structure and organization. Applied behavior analysis (ABA) is one of these treatments; it promotes positive behavior and discourages negative behavior. Occupational therapy can help with life skills like dressing, eating, and relating to people. Sensory integration therapy might help someone who has problems with being touched or with sights or sounds. Speech therapy improves communication skills.
Medications to help with symptoms of ASD, like attention problems, hyperactivity, or anxiety.
Complementary treatments may help boost learning and communication skills in some people with autism. Complementary therapies include music, art, or animal therapy, like horseback riding and even swimming with dolphins.
It is high time that people start to embrace autism and not ostracize such individuals but give more support and kindness. Young children must be taught about it and it’s not a topic to shy away from but accept and cherish that its ok to be different because that way you are special.



0 Comments